CBD in detail
CBD (cannabidial) is one of the least active of the cannabinoids, yet can have dramatic effects on improving ones health. It is a phytocannabinoid and exists in the Cannabis plant in levels of up to 40% of plant extract. It has shown increasing benefits for people suffering from Dravet syndrome, a rare form of epilepsy that plagues people from birth and then continues to get worse. It does so by blocking certain receptors in the brain which scientists are currently trying to pinpoint. It does so without giving off a psychoactive effect like most drugs including other cannabinoids. It has also shown to have anti psychotic effects in patients who suffer from psychosis. It has also shown great benefit in calming the effects of other cannabinoids allowing them to work better as medicine. CBD is also not water soluble similar to other components of the plant a solvent such as pentane or hexane can be used to extract it in pure forms for conducting lab studies. It has also been shown that CBD can be converted into THC when placed under acidic conditions. CBD at room temperature is a clear crystal with no smell and very little to no flavor. When heated to the point of removing the carbolic acid it can turn into a clear liquid or when exposed oxygen it turns to a reddish hue.
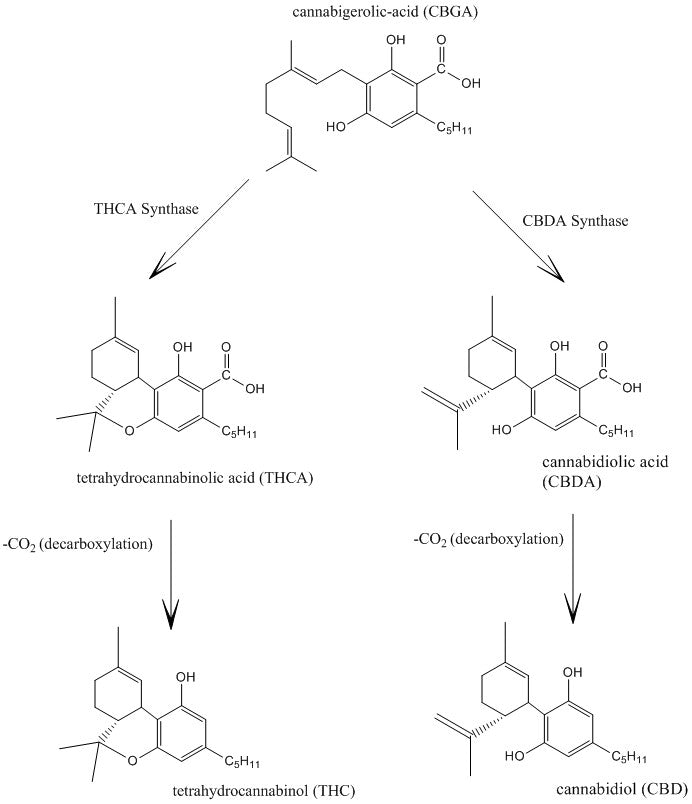
This is an image showing the plants biosynthesis of CBD and THC
Taura, F., Sirikantaramas, S., Shoyama, Y., Yoshikai, K., Shoyama, Y., Morimoto, S. (2007). “Cannabidiolic-acid synthase, the chemotype-determining enzyme in the fiber-type Cannabis sativa”. FEBS Letters 581 (16): 2929–2934. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.05.043 (wikipedia)

Leave a comment